China Relief Map
Map of China > China Locator Map • China Travel Guide • China Relief Map • Beijing Map
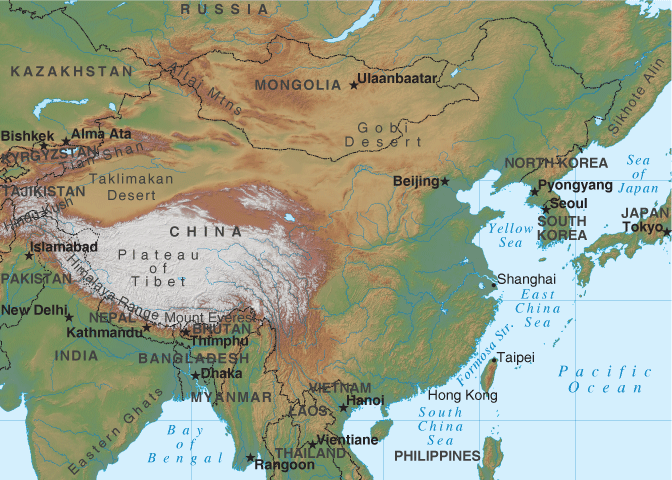
 The first region — the mountains to the west — include the
Plateau of Tibet, the highest region in the world. The melting
snows of the Plateau of Tibet feed rivers such as the Brahmaputra in
India, the Salween in Burma and the Mekong, which snakes through Laos,
Thailand, and Cambodia before ending in Vietnam. The Plateau of
Tibet has about two million inhabitants, most of whom live in the
southern region due to the plateau's unfriendly environment.
The first region — the mountains to the west — include the
Plateau of Tibet, the highest region in the world. The melting
snows of the Plateau of Tibet feed rivers such as the Brahmaputra in
India, the Salween in Burma and the Mekong, which snakes through Laos,
Thailand, and Cambodia before ending in Vietnam. The Plateau of
Tibet has about two million inhabitants, most of whom live in the
southern region due to the plateau's unfriendly environment.
 The second region, extending from the Tarim and Dzungarian Basins to
Northern Manchuria, comprises the type of arid desert environment that
makes agriculture difficult, if not impossible, with the exception of
some types of oasis crops and small farming settlements where grains and
soybeans are grown. Most residents in this area make their living
by keeping sheep, goats, and horses.
The second region, extending from the Tarim and Dzungarian Basins to
Northern Manchuria, comprises the type of arid desert environment that
makes agriculture difficult, if not impossible, with the exception of
some types of oasis crops and small farming settlements where grains and
soybeans are grown. Most residents in this area make their living
by keeping sheep, goats, and horses.
 The third region is home to more than two-thirds of China's
citizens. This part of the country is made up of the plains that
support China's irrigated agriculture, as well as many of the country's
lakes, rivers, and canals that have facilitated transportation and
trade. The "Red Basin" area of this region is home to many of
China's rice fields. In the southern part of this region, residents
enjoy a tropical climate that allows for year-round growing of rice,
sugar, bananas, and tropical fruit.
The third region is home to more than two-thirds of China's
citizens. This part of the country is made up of the plains that
support China's irrigated agriculture, as well as many of the country's
lakes, rivers, and canals that have facilitated transportation and
trade. The "Red Basin" area of this region is home to many of
China's rice fields. In the southern part of this region, residents
enjoy a tropical climate that allows for year-round growing of rice,
sugar, bananas, and tropical fruit.